Balancing Density Control and CO₂ Adsorption Capacity in MOF Synthesis using Multi-Sigma®

This case study showcases how AIZOTH’s AI analytics platform, Multi-Sigma®, is utilized to optimize the synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs), achieving both optimal density and high CO₂ adsorption capacity
1. AI Chain Analysis
The first-stage AI model predicts structural characteristics based on experimental conditions, while the second-stage AI model takes the structural characteristics, which is the output from the first stage, as input to predict functional characteristics.
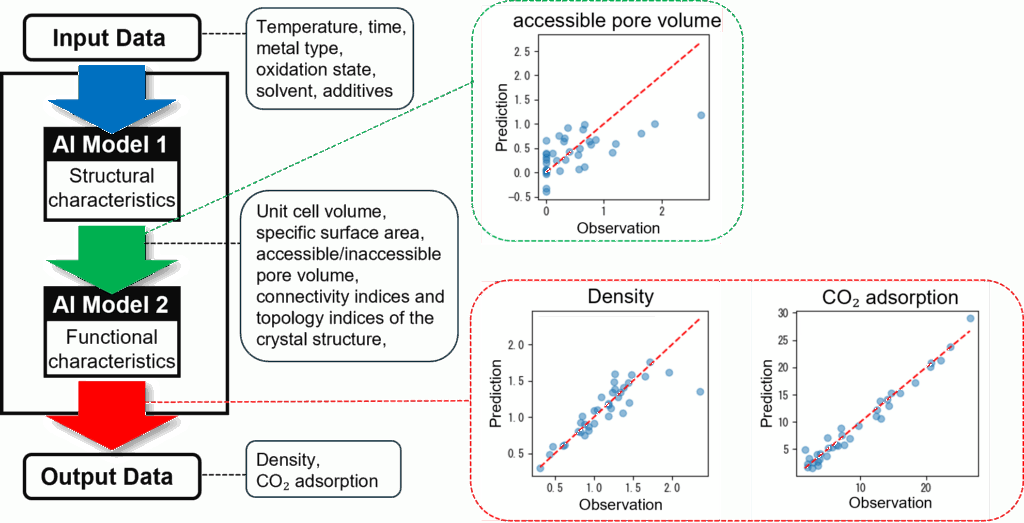
2. Factor Analysis
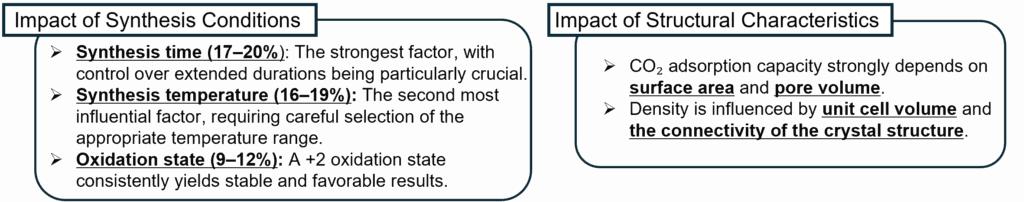
3. Multi-Objective Optimization for CO₂ Adsorption and Density Control
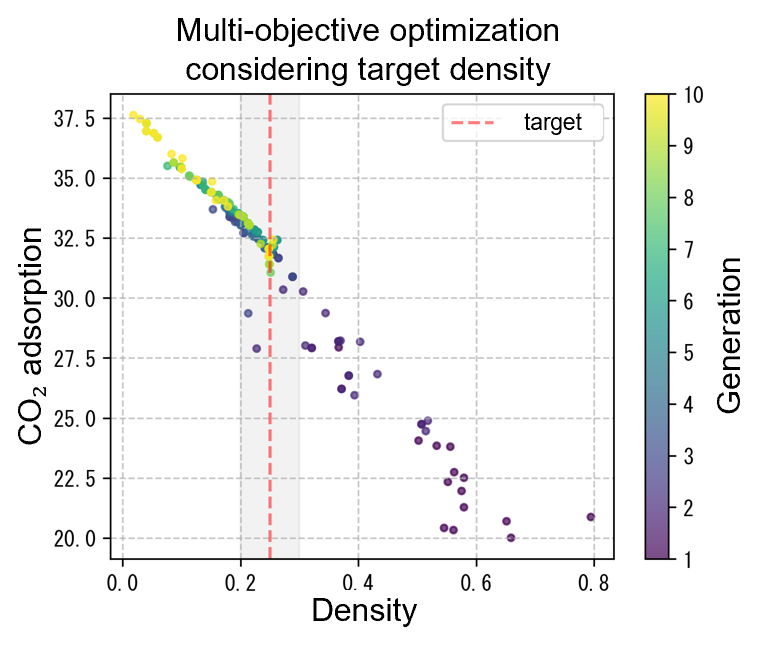
Using Multi-Sigma’s optimization functionality, a multi-objective approach was employed to maximize CO₂ adsorption while maintaining a target density of approximately 0.25 g/cm³. As a result, the following synthesis conditions were identified, achieving a density of 0.25 ± 0.005 g/cm³ and a high CO₂ adsorption capacity of 32.2:
•Synthesis temperature: 174°C
•Synthesis time: 408 hours
•Metal type: Indium
•Oxidation state: +2
(Note 1) Data Source: Kaggle (https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/marquis03/metal-organic-frame-materials-prediction/data)
(Note 2) The unit of density is (g/cm³) and accessible pore volume is (cm³/g)., and the CO₂ adsorption capacity is measured at a temperature of 298 K and a pressure of 16 bar.





