This case study demonstrates how Multi-Sigma® predicts aluminum-alloy mechanical properties, and how it identifies optimal compositions and process parameters while balancing property trade-offs.
1. Building a Performance-Prediction Model Using Multi-Sigma®
We built an AI model that predicts aluminum-alloy mechanical properties (yield strength, tensile strength, elongation) from 24-element composition ratios and eight processing conditions (e.g., solution heat treatment, artificial aging, work hardening). Trained on 450 cases and tested on 50, it achieved reasonably high accuracy.
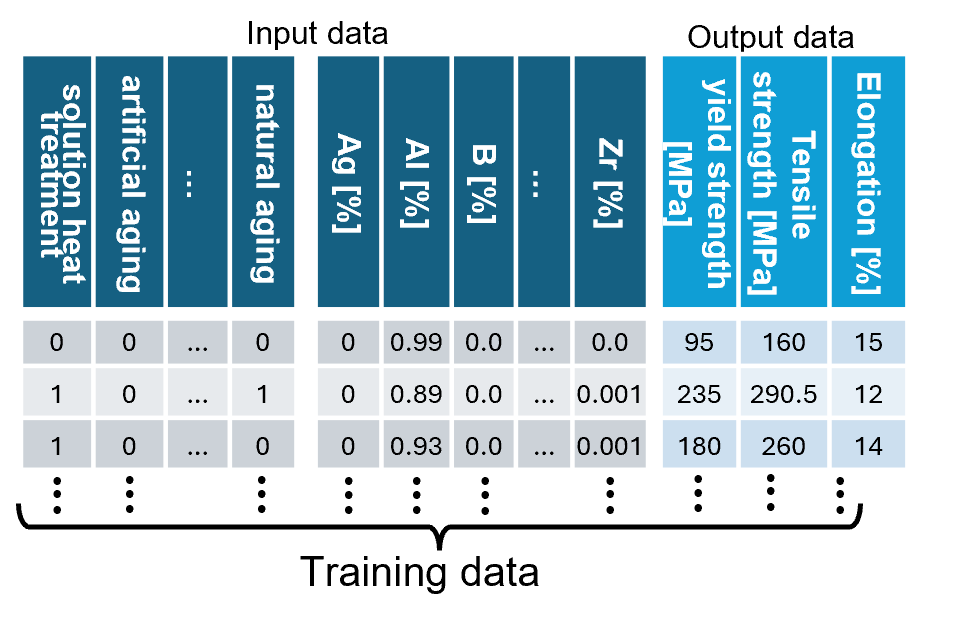


2. Contribution Analysis of Mechanical Properties Using Multi-Sigma®
Using the contribution-analysis feature, we quantitatively evaluated the impact of each element and processing condition on mechanical properties, providing key insights for balancing multi-property trade-offs in materials design.
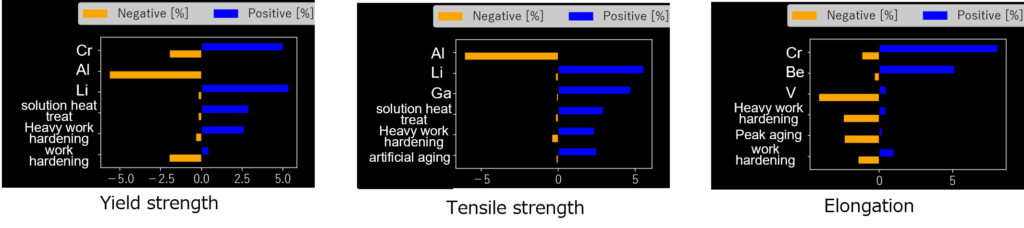
3. Exploring Optimal Composition Ratios and Processing Conditions Using Multi-Sigma®
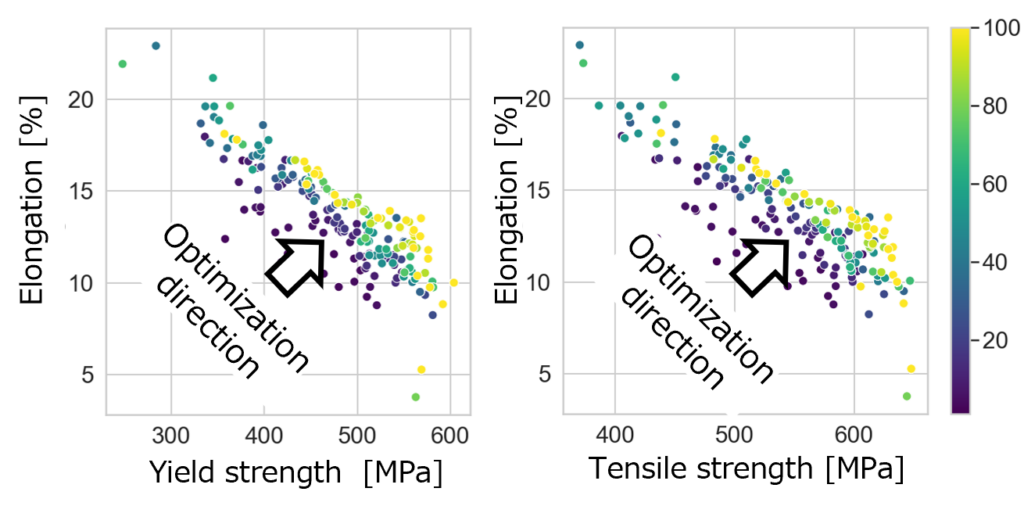
The multi-objective optimization feature enables the simultaneous optimization of yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation. During optimization, constraints can be set so that the total composition sums to 100% and the processing conditions remain realistic. Even when there are trade-offs among properties (e.g., strength vs. ductility), the method presents multiple Pareto-optimal, balanced solutions, allowing flexible selection of the one that best meets the design objectives. Each optimal solution is accompanied by specific composition ratios and processing conditions, providing actionable guidance for reasonable materials design.
Note: The data used in this analysis is processed and edited based on the data published in the article below, under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0) license.
Data source: Bhat, Ninad; Barnard, Amanda; Birbilis, Nick (2023), “Aluminium alloy dataset for supervised learning”, Mendeley Data, V1, doi: 10.17632/b6br4yk6r3.1
