This case study introduces the use of AIZOTH’s AI analytics platform,
Multi-Sigma®, to predict, analyze key factors influencing, and optimize
hydration free energy, a critical property in the drug discovery process.
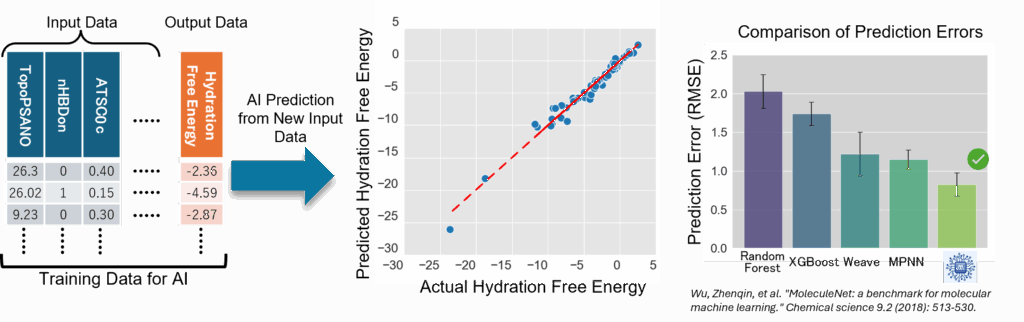
1. Prediction of Hydration Free Energy
The AI prediction capabilities of Multi-Sigma® enable the construction of AI models that capture the
relationship between input data and output data through model training. Using this AI model, it is possible
to accurately predict hydration free energy values from new molecular descriptors.
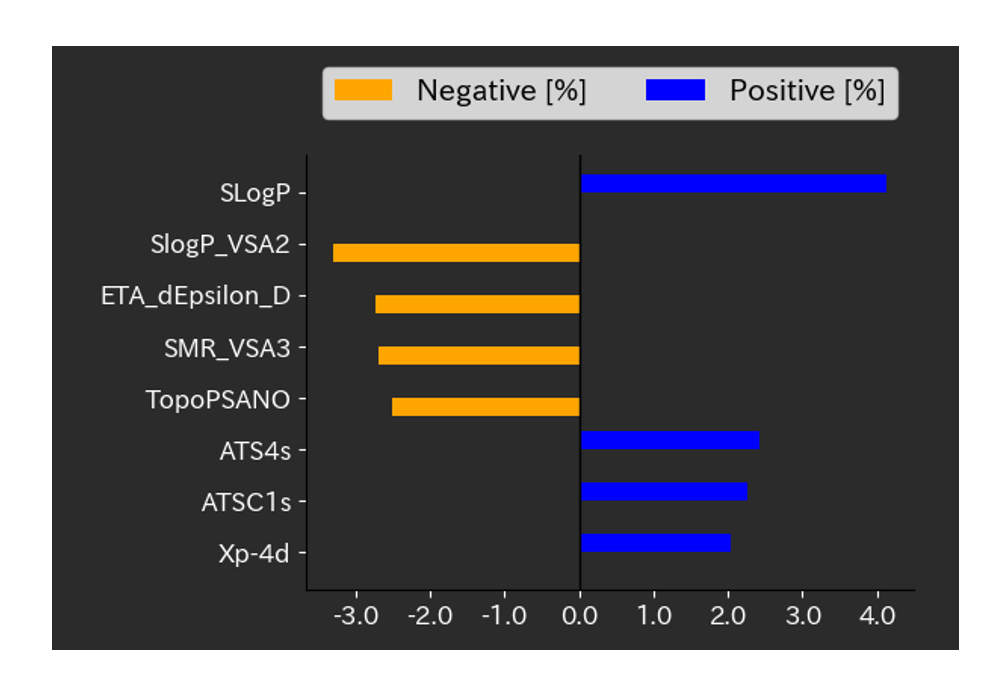
2. Factor Analysis on Hydration Free Energy
The factor analysis functionality of Multi-Sigma® allows the identification of molecular descriptors that positively (and negatively) contribute to hydration free energy.
Strong Positive Influence
1. SLogP: +4.12%
2. ATS4s: +2.42%
3. ATSC1s: +2.25%
4. Xp-4d: +2.04%
Strong Positive Influence
1. SlogP_VSA2: -3.29%
2. ETA_dEpsilon_D: -2.72%
3. SMR_VSA3: -2.68%
4. TopoPSANO: -2.50%
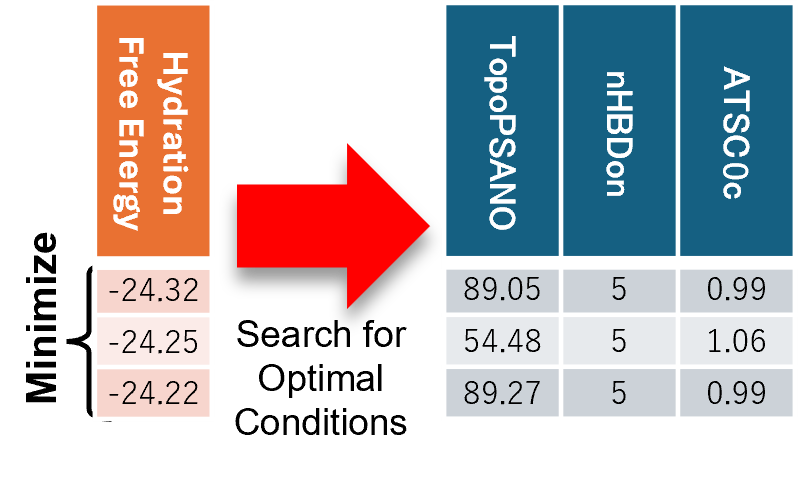
Optimization to Minimize Hydration Free Energy
The optimization functionality of Multi-Sigma® can propose combinations of molecular descriptors that
minimize hydration free energy.
Expected Outcomes:
Significant Streamlining of the Drug Discovery Process
Reduction in Experimental Costs
Realization of Innovative Molecular Design
Shortening of Development Time
Advantages of Optimization with Multi-Sigma®:
For instance, optimization can be conducted under the condition
that nHBDon takes only integer values. Moreover, optimization
can also be carried out by constraining the range of input values.
(Note) Dataset: Molecular data obtained from the NCI database and MoleculeNet. Molecular descriptors calculated using the Mordred module.
Also, data sourced from Kaggle (https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/mmelahi/cheminformatics).
