
At the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), scientists are working on an exciting project to create an artificial heart. They’re using special bearings and smart planning with artificial intelligence to make the artificial heart work better. The goal is to improve both the power of the bearings and how safe the artificial heart is for our blood cells. The team wants to help people who have to wait a long time for a new heart. By combining different areas of expertise, they’re trying to change the way we do heart transplants and make artificial hearts a more hopeful option for people with heart problems.
Challenges
・Heart diseases are a major cause of death in Japan, and the prolonged waiting period for heart transplants necessitates the development of an artificial heart using hydrodynamic bearings.
・The design of hydrodynamic bearings involves numerous design parameters and optimizing them through trial and error has its limitations.
There are 7,200 combinations of input conditions, including groove number (3-18, 16 options), groove angle (10-180 degrees, 18 options), groove entrance depth (0.05-0.25 mm, 5 options), and groove exit depth (0.05-0.25 mm, 5 options).
Solutions
Using an innovative experimental planning method leveraging AI, we conducted an analysis combining neural networks and multi-objective genetic algorithms. Based on a minimal set of 30 to 60 simulation experiments, we optimized complex designs with multiple inputs and objectives. Using AI analysis through Multi-Sigma from Aizoth Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Tsukuba, Ibaraki), we achieved efficient analyses, showcasing the power of AI in optimizing intricate designs.
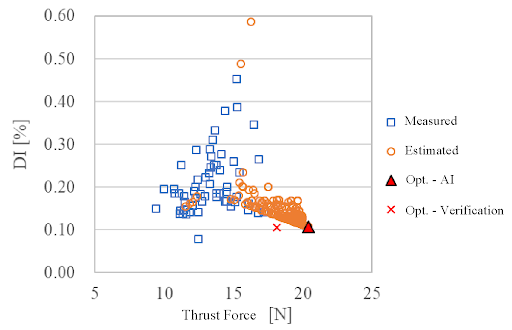
Results
We used a neural network to create an AI predictive model and then employed a multi-objective genetic algorithm to find the optimal design for hydrodynamic bearings. Our goal was to simultaneously increase generating force and reduce red blood cell damage. Contrary to conventional thinking that more grooves are better, our AI-driven factor analysis revealed the crucial role of groove depth, challenging traditional design guidelines. Comparing the new designs to conventional ones showed potential improvements in both generating force and reducing red blood cell damage. Despite the usual belief, our results suggested that designs with greater groove depth could be more effective. Through analyses based on 30 to 60 iterations for each of the 7,200 combinations, we efficiently optimized the design, achieving innovative solutions with less than 1/100th of the typical effort, showcasing the transformative impact of AI in discovering efficient designs.
The Multi-Sigma Advantage
Ready to revolutionize your Chemical Engineering processes? Contact us to start your free trial with AIZOTH’s Multi-Stigma today. Experience the difference as you elevate decision-making, unlock unprecedented benefits, and redefine the future of Chemical Engineering with the power of AI.
Start Your Free Trial Now